CRISPR gene editing method applied to humans
Chinese researchers have launched the first-ever human experiment using CRISPR-Cas9 technology. A patient with an aggressive form of lung cancer was given altered immune cells. Researchers from Sichuan University hope that by modifying one of the genes, the patient’s body will be able to cope with the cancer on its own.
Oncologist Lu You is responsible for the experiment. SyndromeóUnder his direction, through the CRISPR-Cas9 method, he modified cellsóimmune cells switching off the PD-1 protein of a patient with non-small cell diseaseómetastatic lung cancer, in whichóthat chemotherapy and radiotherapy have failed. PD-1 is a protein thatóre inhibits the body’s defense mechanism, thus creating good conditions for cancer growth.
The study involves ten patientsów. The health status of sick waspsób will be monitored on an ongoing basis. To evaluate whether CRISPR-Cas9 method is effective in humans. If the experiment is successful, it will be a breakthrough in the treatment of many diseasesób, from whichóand the current situation is not well managed by mankind.
What it in ogóThis is the CRISPR?
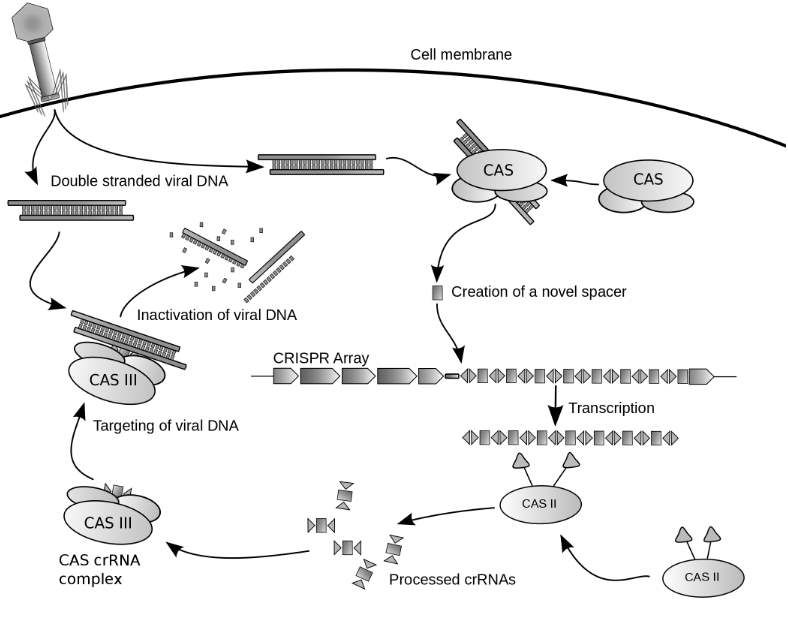
CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) is a system used by bacteria to defend themselves against viruses. It’s a defense mechanism, a repetitive sequence of fragmentsóin DNA. It was noticed by Yoshizumi Ishino in the late 1980s. Last century in the genome of Escherichia coli. Thesis mechanism includes information about DNA virusóin and in combination with a DNA-cutting enzyme – Cas9 endonuclease is a defence system against viruses.
The method itself, called CRISPR-Cas9, works by recognizing foreign DNA through mRNA, whichóresponsible for carrying genetic information. The entire CRISPR sequence is then split into crótighter pieces (crRNA) containing the viral DNA fragment and the CRISPR sequence. Based on this information contained in the CRISPR sequence, a tracrRNA is created, który attaches itself to crRNA, whichóThe cells together form gRNA and któThe horizontal bar indicated that the horse felt the chill, and the probe will be exposed to many dangerous influencesówhich in turn is remembered by the cellóand used in the fight against the virus.
In the case of gRNA infections, whichówhich is a model of the attacking virus combines with the Cas9 enzyme and cuts the attacker into pieces, completely inactivating it. The excised pieces are then added to the CRISPR sequence, a kind of threat database. The graphic below explains everything.
During further development of the technique it turned out that gRNA can be created by humans, thanks to which we can interfere in genes, substitute or cut dangerous fragments. This method is cheaper and more precise than those used previously.